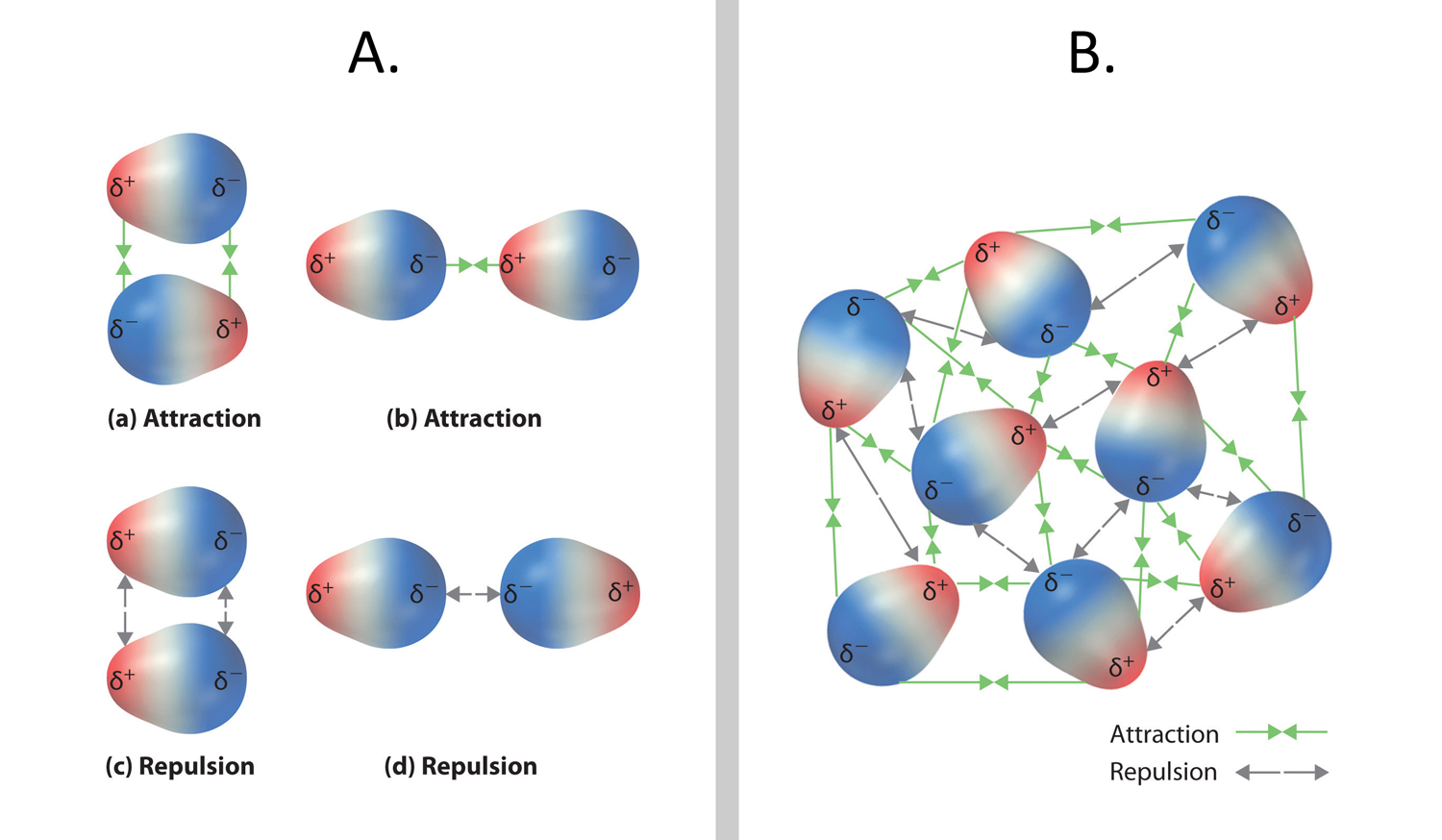
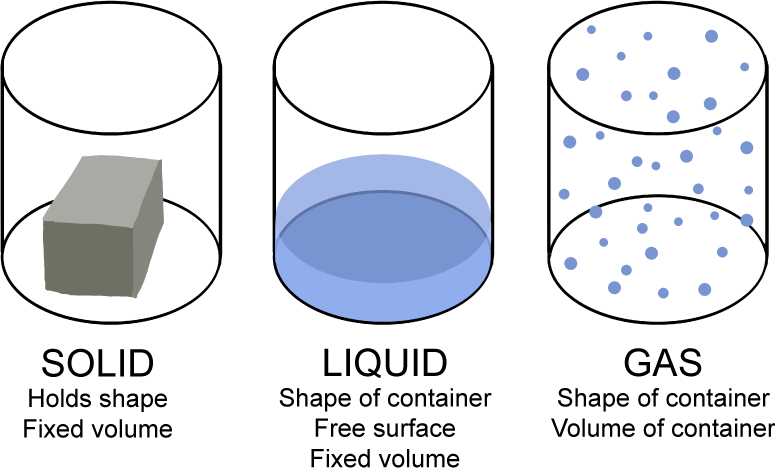
Solids. The properties of solids include: Solids stay in one place and can be held. Solids always take up the same amount of space. In chemistry, Henry's law is a gas law that states that the amount of dissolved gas is proportional to its partial pressure in the gas phase. The proportionality factor is called the Henry's law constant. It was formulated by the English chemist William Henry, who studied the topic in the early 19th century. In his publication about the quantity of gases absorbed by water, he described the. Properties and characteristics of common industrial gases oxygen, o2, nitrogen, n2, argon, ar, carbon dioxide, co2, hydrogen, h2, gas, liquid, uses and applications. The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from liquid to gas throughout the bulk of the liquid. At the boiling point molecules anywhere in the liquid may be vaporized. Learn about solids, liquids and gases as you experiment with the conditions that change them from one form to another in this fun, interactive science activity. Water is a common example as it exists in all three forms, youve no doubt seen it as ice, liquid water and steam. At low pressures and relatively high temperatures, the volume of most gases is so large that the volume of the molecules themselves may be neglected. Nov 21, 2003An interactive experiment in which children aged 910 can heat and cool a coloured gas to see how it behaves. A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. The volume is definite if the temperature and pressure are constant. When a solid is heated above its melting point, it becomes liquid, given that the pressure is higher than the triple point of the substance. Title Solids, Liquids, and Gases By LeShawna K. Coleman Solids, Liquids, and GasesSecond GradeRhonda ElLeShawna K. ColemanWritten November 7, 2000 Looking for a Gas Gases are everywhere. You may have heard about the atmosphere. The atmosphere is an envelope of gases that surrounds the Earth. Gases are a state of matter characterized by two properties: their lack of definite volume and their lack of definite shape. This definition suggests, in the first place, that a given mass of gas can occupy any volume whatsoever. Musthave reference for processes involving liquids, gases, and mixtures. Reap the timesaving, mistakeavoiding benefits enjoyed by thousands of chemical and process design engineers, research scientists, and educators. Buy Gases, Liquids and Solids: And Other States of Matter on Amazon. com FREE SHIPPING on qualified orders Drying of organic liquids such as LPG, propylene, butane, steam cracked liquids, gasoline and fluorinated hydrocarbons, aromatic solvents; Drying of industrial gases, including steam cracked gases, catalytic reforming recycle gas, synthesis gas, methyl chloride, LNG, etc. The particle theory is used to explain the properties of solids, liquids and gases. The strength of bonds between particles is different in all three states. THE 9 CLASSES OF DANGEROUS GOODS Dangerous goods are materials or items with hazardous properties which, if not properly controlled, present a potential hazard to human health and safety, infrastructure and or their means of transport. A block of wood, milk, and air all have properties. All the material on earth is in three statessolid, liquid, and gas. The state of the matter refers to the group of matter with the same properties. Explore molecule shapes by building molecules in 3D! How does molecule shape change with different numbers of bonds and electron pairs? Find out by adding single, double or triple bonds and lone pairs to the central atom. Then, compare the model to real molecules. Primary Resources free worksheets, lesson plans and teaching ideas for primary and elementary teachers. Liquid Basics Liquids are the second state of matter we will talk about. Solids are objects you can hold and maintain their shape. Gases are floating around you or trapped in bubbles. Liquids are found between the solid and gas states. Examples of liquids at room temperature include water (H 2 O), blood, and even honey. If you have different types of molecules dissolved in a liquid, it is. Cluster Structure and properties: The abundance distributions for several kinds of clusters show that there are certain sizes of clusters with exceptional stability, analogous to the exceptional stability of the atoms of the inert gases helium, neon, argon, krypton, and xenon and of the socalled magic number nucleii. , the sequence of unusually stable atomic nuclei beginning with the. Properties, uses and applications of nitrogen gas and nitrogen liquid. UIG is a supplier of nitrogen and other industrial gases, new and used industrial gas plants and plant components plus related engineering, construction, operation, and maintenance services..